Understanding "Radiant Heat"
Radiant Heating Defined
Radiant heating operates through the transfer of thermal energy via electromagnetic waves, distinguishing it as one of the three primary heat transfer methods alongside conduction and convection. Unlike conduction, which requires direct contact between objects, or convection, which relies on the movement of fluids or gases, radiant heating transfers energy through empty space.
This process is governed by the laws of thermodynamics, which state:
"Heat always moves from warmer bodies to cooler ones when a temperature differential exists."
You can see this principle at work when you feel the warmth of the sun on your skin during a cool day, even though the air around you remains chilly. Radiant heating systems harness this natural phenomenon, providing an efficient and comfortable way to warm indoor spaces by directly transferring heat to objects and surfaces.


The Warmth of Nature
People often compare radiant heat to the warmth you feel from the sun on a sunny day - direct and comforting!
Radiant Heating in HVAC
These systems radiate heat from surfaces such as floors, walls, or ceilings, much like the comforting warmth you feel from the sun or a cozy fireplace. Unlike conventional systems that prioritize heating the air, radiant heating focuses on directly warming people and objects, delivering an energy-efficient and comfortable heating solution.
Types of Radiant Heating Systems
Radiant heating can be implemented in two primary ways:
- Electric
- Hydronic
Electric Radiant Heating
One of the key advantages of electric radiant heating is its straightforward installation and precise control, making it an ideal choice for smaller spaces or specific areas like bathrooms. These systems are especially popular for creating warm floors in tiled areas, providing localized comfort rather than serving as a primary heating solution.
However, electric radiant heating is generally less energy-efficient than hydronic systems, which use heated water circulated through pipes. This reduced efficiency makes electric systems more expensive to operate over time, particularly in larger spaces or for whole-home heating. As a result, they are best suited for targeted applications where convenience and comfort outweigh long-term operational costs.
Hydronic Radiant Heating
Hydronic radiant heating involves a closed-loop PEX tubing system that circulates heated water.
Contractors install this system within the floor or ceiling of a building.
Hydronic System Efficiency
Hydronic radiant heating systems are renowned for their exceptional efficiency. Water's high thermal capacity allows it to store and transport heat far more effectively than air, making it an ideal medium for heating. This efficiency enables hydronic systems to use a small, energy-efficient pump to circulate heated water through pipes, minimizing energy consumption.
In contrast, traditional HVAC systems rely on large fans and extensive ductwork to distribute warm air, which often leads to significant heat loss during transit. By eliminating this inefficiency, hydronic systems not only reduce energy costs but also deliver consistent and evenly distributed warmth.
Additionally, the versatility of hydronic systems makes them suitable for various applications, from underfloor heating to radiant ceiling panels, offering a quiet, clean, and effective heating solution for residential and commercial spaces alike.
Hydronic Radiant Ceiling Heating
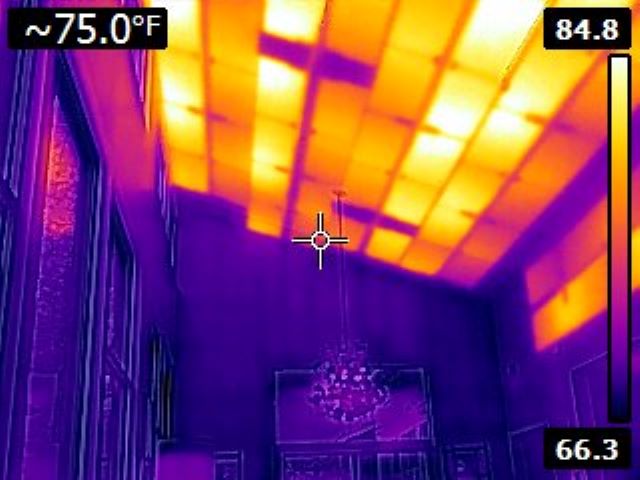


Radiant ceiling panels, are commonly used for ceiling installations. These panels are seamlessly integrated into the ceiling structure and typically covered with drywall, preserving the aesthetics of the room.
Additionally, as the heat radiates from the ceiling, it encounters fewer obstructions and provides a larger, unobstructed radiant surface. Importantly, radiant heat, being an electromagnetic phenomenon, travels downwards effectively, ensuring a comfortable, well-heated space regardless of the ceiling height.
Messana Ray Magic® NK radiant ceiling panels
High-efficiency radiant ceiling panels, such as Messana Ray Magic® NK, deliver excellent heat transfer and outperform many other ceiling systems in both energy efficiency and overall performance. Additionally, these ceiling panels excel in radiant cooling applications.
Hydronic Radiant Floor Heating
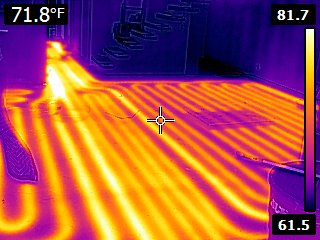
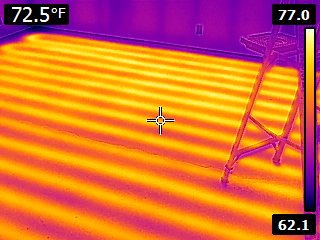
Hydronic contractors implement hydronic radiant floor heating through several methods, including floor panels, underfloor tubing, concrete-based systems, or a gypsum pour (gypcrete).
Radiant floor offers the comfort of warm floors underfoot, an especially appreciated feature in bathrooms and other tiled spaces. However, it’s important to note that floor installations may limit flooring choices due to heat conductivity considerations and limitations on maximum floor temperatures for certain materials, such as wood.
Furthermore, the added thermal mass of certain systems or materials, such as concrete, gypcrete, tiles, or stones, can make the system slower to react compared to ceiling installations. This responsiveness may be an important consideration depending on your heating needs and lifestyle.
Radiant Heating In Reverse = Radiant Cooling!
Hydronic Radiant Systems can be used for both heating and cooling! By employing a chilled radiant surface, thermal energy will be radiated from objects/occupants in a room, to the chilled surface.
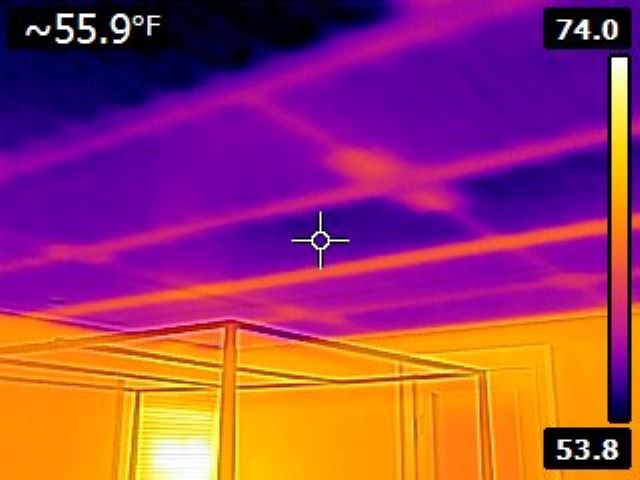


Conclusion
Radiant heating systems, whether electric or hydronic, ceiling or floor, offer a unique comfort unmatched by traditional HVAC systems. In essence, by directly warming people and objects, radiant heating provides a consistent, comfortable heat that closely mimics natural solar radiation.
Finally, at Messana Hydronic Technologies, our team of experts specialize in designing hydronic radiant cooling and heating systems. We’re here to help you navigate the options and determine the best solution for your specific needs and space.
Interested in learning more?
We offer a free consultation and free estimate. Without delay, get a free estimate from our team today!
Hydronic radiant cooling and heating systems are an investment in comfort and efficiency, providing you with a superior heating solution. Trust Messana to guide you on this journey to ultimate indoor comfort.